The budgeted price is usually based on standard cost – what your company expects to pay per unit of material. Picture this—your direct materials end up costing more than expected, but you’re not sure why or by how much. That’s where understanding and computing the price variance becomes essential. However, someone other than purchasing manager could be responsible for materials price variance. For example, production is scheduled in such a way that the purchasing manager must request express delivery. In this situation the production manager should be held responsible for the resulting price variance.

Steps to Calculate Material Price Variance
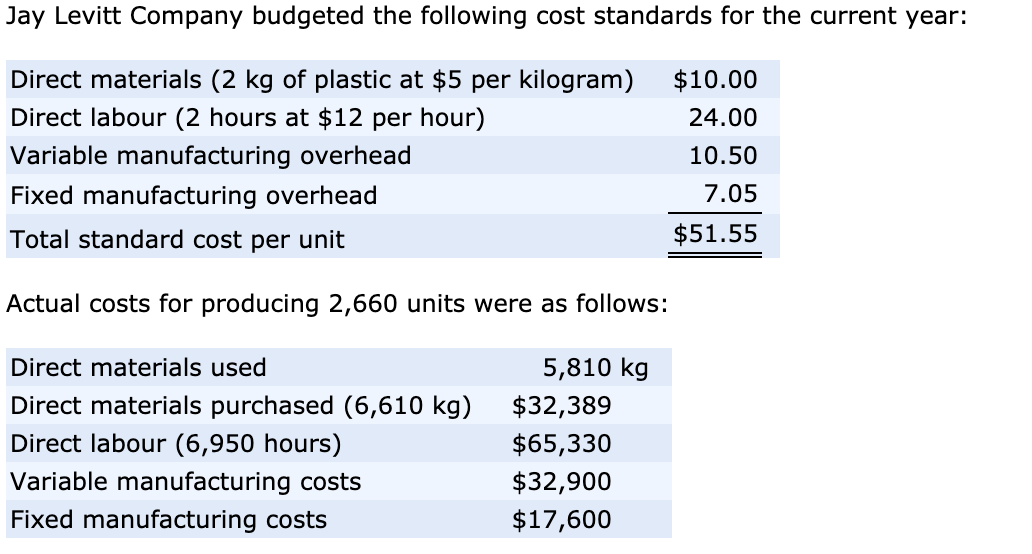
The actual cost less the actual quantity at standard price equals the direct materials price variance. The difference between the actual quantity at standard price and the standard cost is the direct materials quantity variance. The difference in the quantity is multiplied by the standard price to determine that there was a $1,200 favorable direct materials quantity variance.
Related AccountingTools Courses
To calculate the material price variance, you must first know how much product your company used. You’ll need to gather data on the actual quantity of materials employed in production. Internal factors, such as production efficiency and waste management, significantly affect material quantity variance. Inefficient production processes, outdated machinery, or inadequate employee training can result in higher material consumption than planned. Implementing lean manufacturing techniques, investing in modern equipment, and providing ongoing training for employees can enhance production efficiency and reduce material waste. Additionally, regular audits of the production process can identify areas for improvement and help maintain optimal material usage.
Implications of direct material price variance
This amount will represent the expected expenditure on direct material for this many units. The difference between this actual expenditure and the actual expenditure on direct material is the direct materials price variance. Because the company uses 30,000 pounds of paper rather than the 28,000-pound standard, it loses an additional $20,700. To compute the direct materials price variance, subtract the actual cost of direct materials ($297,000) from the actual quantity of direct materials at standard price ($310,500). This difference comes to a $13,500 favorable variance, meaning that the company saves $13,500 by buying direct materials for $9.90 rather than the original standard price of $10.35. Direct material price variance is calculated to determine the efficiency of purchasing department in obtaining direct material at low cost.
You compare this with the “actual price,” what you actually end up paying. A favorable material price variance suggests cost effective procurement by the company. Direct Material Price Variance (DMPV) shows the amount by which the total cost of raw materials has deviated from the planned cost as a result of a price change over a period. An unfavorable one might show supplier problems or rising costs in the industry. Let’s say your company set a budget of $5 for a pound of copper, but the market rates went up, and you ended up paying $6 per pound. To figure out the variance, subtract that actual price ($6) from the budgeted price ($5), giving you a difference of $1 per pound.
About Dummies
- Finance Strategists has an advertising relationship with some of the companies included on this website.
- A favorable material price variance suggests cost effective procurement by the company.
- The actual cost less the actual quantity at standard price equals the direct materials price variance.
- Direct materials quantity variance is also known as direct material usage or volume variance.
- In a multi-product company, the total quantity variance is divided over each of the products manufactured.
- This ensures that the entire gain or loss on the procurement of materials is reflected in the results of the current period.
Sharing variance reports and findings with relevant departments fosters a collaborative environment where everyone is aware of cost control objectives. For instance, procurement teams can work closely with suppliers to negotiate better prices, while production teams can implement process improvements to reduce material waste. fixed asset turnover ratio formula calculator This cross-functional collaboration ensures that all aspects of the business are aligned towards achieving cost efficiency. This setup explains the unfavorable total direct materials variance of $7,200 — the company gains $13,500 by paying less for direct materials, but loses $20,700 by using more direct materials.
The budgeted price is the price that the company’s purchasing staff believes it should pay for a direct materials item, given a predetermined level of quality, speed of delivery, and standard purchasing quantity. Thus, the presence of a direct material price variance may indicate that one of the underlying assumptions used to construct the budgeted price is no longer valid. The direct material price variance is one of two variances used to monitor direct materials. Thus, the price variance tracks differences in raw material prices, and yield variance tracks differences in the amount of raw materials used. The left side of the DMPV formula estimates what the actual quantity of direct materials purchased should cost according to the standard price allowed in the budget. The right side of the formula calculates what the direct materials actually cost during the period.
Direct material price variance is the difference between actual cost of direct material and the standard cost. Actual cost of material is the amount the company paid to supplier to get input for the prodution. Standard cost is the amount the company expect to pay to get the same quantity of material. The difference of actual and standard cost raise due to the price change, while the material quantity remains the same.
That means the company spent less on materials than expected – a good thing! The result from this calculation gives you the direct material price variance for your accounting records. If materials cost more than planned, your variance will be negative, showing a loss against your standard cost. It’s important to note that direct material variance can be broken down into more specific components, such as price and quantity variances. However, the initial calculation provides a broad overview that can guide more detailed analysis. By regularly monitoring these variances, businesses can quickly identify trends or anomalies that may indicate underlying issues, such as supplier problems or inefficiencies in the production process.
The difference between the expected and actual cost incurred on purchasing direct materials, expressed as a positive or negative value, evaluated in terms of currency. The direct material price variance is favorable if the actual price of materials is __________ than the standard price. As businesses strive for greater precision in cost management, advanced techniques in variance analysis have become increasingly valuable. One such technique is the use of trend analysis, which involves examining variance data over multiple periods to identify patterns and trends.