If you use the double-declining balance method to calculate the value of depreciation, the value would be high in the initial years. However, it will reduce year after year as the asset gets older. Various software tools and online calculators can simplify the process of calculating DDB depreciation. These tools can automatically compute depreciation expenses, adjust rates, and maintain depreciation schedules, making them invaluable for businesses managing multiple depreciating assets.
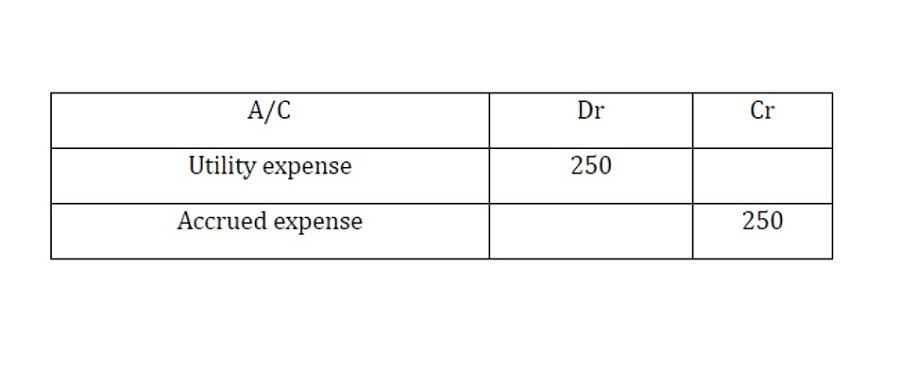
How to calculate depreciation using the double declining method
You bought and placed in service $2,890,000 of qualified farm machinery in 2023. Your spouse has a separate business, and bought and placed in service $300,000 of qualified business equipment. This is because you and your spouse must figure the limit as if you were one taxpayer. You reduce the $1,160,000 dollar limit by the $300,000 excess of your https://www.bookstime.com/articles/investing-activities costs over $2,890,000. When you use property for both business and nonbusiness purposes, you can elect the section 179 deduction only if you use the property more than 50% for business in the year you place it in service. If you use the property more than 50% for business, multiply the cost of the property by the percentage of business use.
Double Declining Balance Method vs. Straight Line Depreciation
The following is a list of the nine property classifications under GDS and examples of the types of property included in each class. These property classes are also listed under column (a) in Section B of Part III of Form 4562. For detailed information on property classes, see Appendix B, Table of Class Lives and Recovery Periods, in this publication.
Sum-of-the-Years’ Digits Method
Tax depreciation 101 – Thomson Reuters Tax & Accounting
Tax depreciation 101.
Posted: Thu, 24 Aug 2023 07:00:00 GMT [source]
This section discusses the rules for determining the depreciation deduction for property you place in service or dispose of in a short tax year. It also discusses the rules for determining depreciation when you have a short tax year during the recovery period (other than the year the property is placed in service or disposed of). Instead of using the above rules, you can elect, for depreciation purposes, to treat the adjusted basis of the exchanged or involuntarily converted property as if disposed of at the time of the exchange or involuntary conversion. Treat the carryover basis and excess basis, if any, for the acquired property as if placed in service the later of the date you acquired it or the time of the disposition of the exchanged or involuntarily converted property. The depreciable basis of the new property is the adjusted basis of the exchanged or involuntarily converted property plus any additional amount you paid for it. The election, if made, applies to both the acquired property and the exchanged or involuntarily converted property.
Adjustments and Exceptions in DDB Calculation
This chapter explains how to determine which MACRS depreciation system applies to your property. It also discusses other information you need to know before you can figure depreciation under MACRS. This information includes the property’s recovery class, placed in service date, and basis, as well as the applicable recovery period, convention, and depreciation method. It explains how to use this information to figure your depreciation deduction and how to use a general asset account to depreciate a group of properties.

The 37th day of the last quarter is November 25, which is the midpoint of the quarter. November 25 is not the first day or the midpoint of November, so Tara Corporation must treat the property as placed in service in the middle of November (the nearest preceding double declining depreciation first day or midpoint of that month). A quarter of a full 12-month tax year is a period of 3 months. The first quarter in a year begins on the first day of the tax year. The second quarter begins on the first day of the fourth month of the tax year.

- This depreciation method is used when assets are utilized more in the early years and when assets become obsolete quickly.
- Whether you’re a business owner, an accounting student, or a financial professional, you’ll find valuable insights and practical tips for mastering this method.
- For example, if you depreciate your machine using straight line depreciation, your depreciation would remain the same each month.
- In May 2023, Sankofa sells its entire manufacturing plant in New Jersey to an unrelated person.
- It is determined based on the depreciation system (GDS or ADS) used.
However, it does not reflect any reduction in basis for any special depreciation allowance.. An addition or improvement you make to depreciable property is treated as separate depreciable property. Its property class and recovery period are the same as those that would apply to the original property if you had placed it in service at the same time you placed the addition or improvement in service. The recovery period begins on the later of the following dates.
However, do not increase your basis for depreciation not allowed for periods during which either of the following situations applies. To be depreciable, property must have a useful life that extends substantially beyond the year you place it in service. At the end of their useful lives, when the cars are no longer profitable to lease, Maple sells them. Maple does not have a showroom, used car lot, or individuals to sell the cars.
- Silver Leaf, a retail bakery, traded in two ovens having a total adjusted basis of $680, for a new oven costing $1,320.
- What it paid to acquire the asset — to some ultimate salvage value over a set period of years (considered the useful life of the asset).
- For this purpose, however, treat as related persons only the relationships listed in items (1) through (10) of that discussion and substitute “50%” for “10%” each place it appears.
- Go to IRS.gov/Account to securely access information about your federal tax account.
- However, you should be aware of the method your company uses to maintain its books of accounts.
- The basis for depreciation of MACRS property is the property’s cost or other basis multiplied by the percentage of business/investment use.